FTP 101 - part 4: Using basic FTP commands
Published {$created} by Carsten Blum
So far in our FTP 101 series, we’ve looked at how FTP connections work, the difference between ASCII and Binary transfer modes, and why plain FTP isn’t secure.
Today, we’re getting hands-on.
Prefer hands-on over reading tutorials? ftpGrid is built to be intuitive — create a free account and get started instantly.
This post will walk you through the most essential FTP commands so you can upload, download, and manage files from any command-line FTP client.
Create your first FTP account
But before we get that far, we need to create a new FTP account.
Sign up or log in to https://app.ftpgrid.com/auth/login
Go to your account dashboard at https://app.ftpgrid.com/app/ftpaccounts
Create a new FTP Account. "FTP Account" is just our word for an edge service account and is used for both FTP, SFTP and SCP. But int this instance it actually just an FTP account.
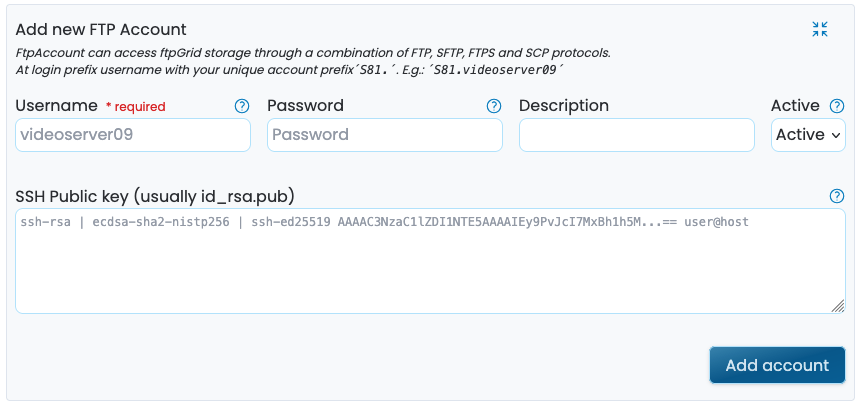
Fill in the user user you want, for instance you name. When logging in you need to prefix the username with your unique account prefix.
Make the password long and complex, ftp is inherently insecure, but you can mitigate this with some complexity in your passwords.
Connecting to an FTP server
To start, open your terminal and type below command, where edgeN is your assigned edge server, for instance edge7.ftpgrid.com:
ftp edgeN.ftpgrid.comYou’ll be prompted for your username and password, which we created initially. After logging in, you’ll land in the default directory on the server.
If you need to enable passive mode (which you certainly do if you’re behind a firewall or NAT), type:
passivePassive mode usually required for downloads to work properly on modern networks.
Listing files and directories
Want to see what’s on the server? Use:
lsThis lists files and folders in the current directory. If you want to change directories:
cd foldernameTo confirm where you are:
pwdThese commands are adopted from basic UNIX and Linux commands. Cd = change directory, pwd = print working directory
Uploading a file to the server
To upload a single file from your local machine to the server, use:
put myfile.txtNeed to upload multiple files at once?
mput *.txtThis uploads all .txt files in the current local directory. You may be prompted to confirm each one – type y to proceed. Remember to set the right transfer mode before uploading - ascii or binary.
Downloading files from the server
To download a single file to your local machine:
get report.csvOr, to download multiple files at once:
mget *.csvAgain, you’ll likely be prompted to confirm each file. Use ascii or binary mode as appropriate before downloading.
Deleting files (with caution!)
Be cautious, because on FTP servers there are no "trash bin" where you can recover your files from.
To delete a file from the server:
delete oldfile.txtTo remove a directory:
rmdir oldfolderYou can also create new directories:
mkdir newfolderBe careful! There’s no undo button in FTP!
Closing the session
When you’re done, simply type:
byeor:
quitThis cleanly disconnects from the FTP server and closes your session.
Most useful FTP commands – quick reference
Action | Command |
|---|---|
Connect | ftp edgeN.ftpgrid.com |
List files | ls |
Change directory | cd foldername |
Upload file | put filename.txt |
Upload multiple | mput *.txt |
Download file | get filename.txt |
Download multiple | mget *.log |
Delete file | delete filename.txt |
Make folder | mkdir foldername |
Remove folder | rmdir foldername |
Switch to ASCII | ascii |
Switch to Binary | binary |
Passive mode | passive |
Disconnect | bye or quit |
In upcoming tutorials we'll deep dive in to some of these commande, as well as look at how FTP can be used at a storage solution for video surveillance cameras.
Thanks for reading, and make sure to check out our other tutorials here.